|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
This post was first published on Medium.
Boneh-Lynn-Shacham (BLS) is a signature scheme based on bilinear pairings.
Compared to ECDSA or Schnorr signatures, it enjoys several salient advantages:
- 2 times shorter
- friendly to signature and key aggregation
- deterministic: it does not rely on random number generators.
Due to its minimal storage and bandwidth requirements, it has been adopted by multiple blockchains such as Ethereum, Dfinity, Algorand, and Chia. We illustrate how to implement it on Bitcoin natively.
BLS Signatures: the Theory
Hash to Curve: H(m)
In ECDSA, a message m is hashed into a number. In BLS, we hash it to a point on the elliptic curve.
One naive way is to hash the message and multiply the result with the generator point G to get a curve point. However, it is insecure.
To do this securely, we first hash the message using SHA-256 and treat the 256 bit result as the x-coordinate of a point. If no such point exists on the curve, we increment the x-coordinate and try again, till we find the first valid point¹.
Sign
Signing is trivial. We simply multiply:
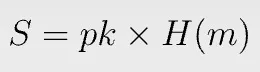
pk is the private key and m is the message. Note no random number is needed. S is just a curve point and can be compressed to 33 bytes, about half the size of an ECDSA signature.
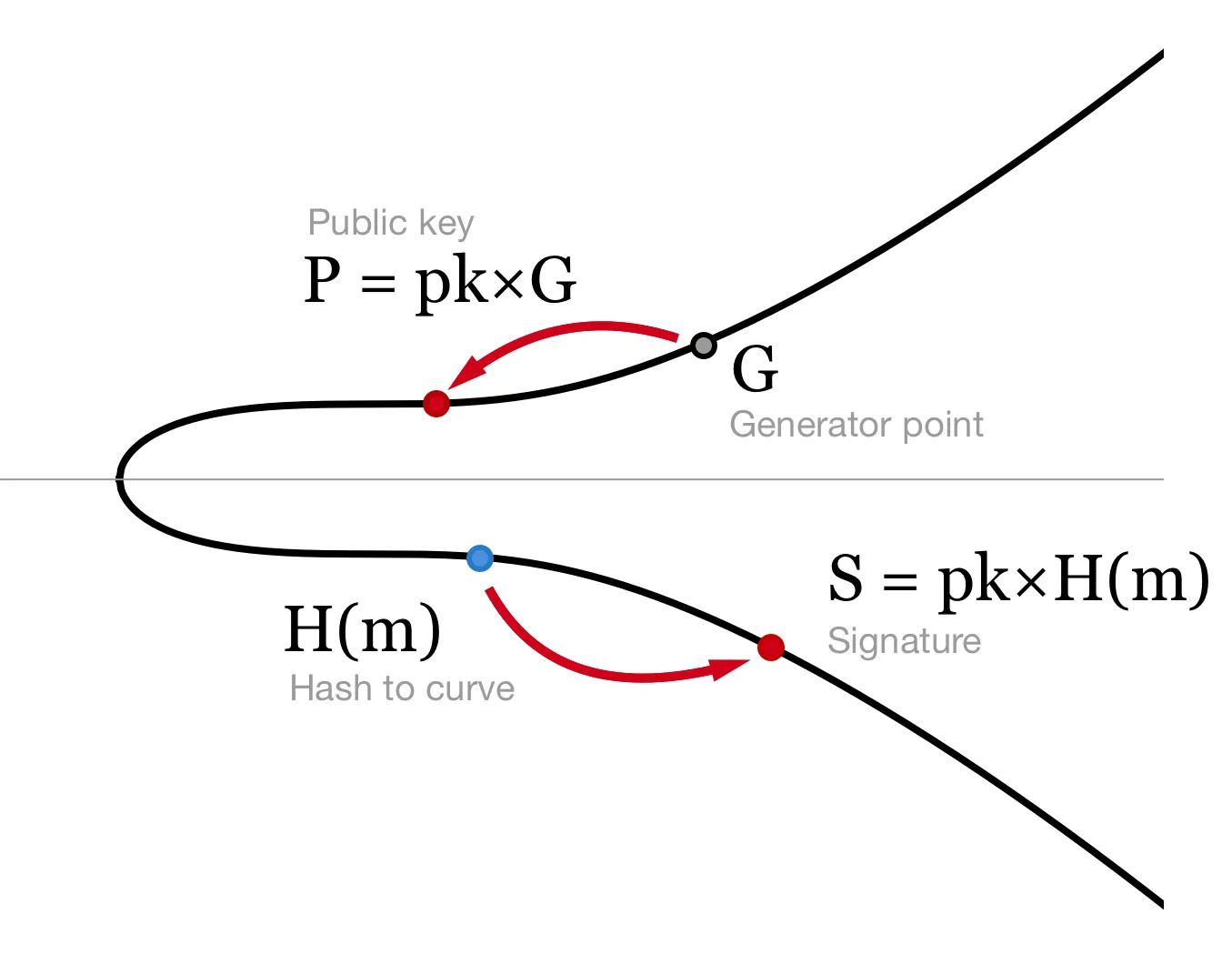
Verify
To verify a signature, we simply compare two pairings:
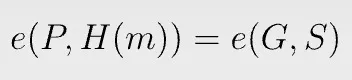
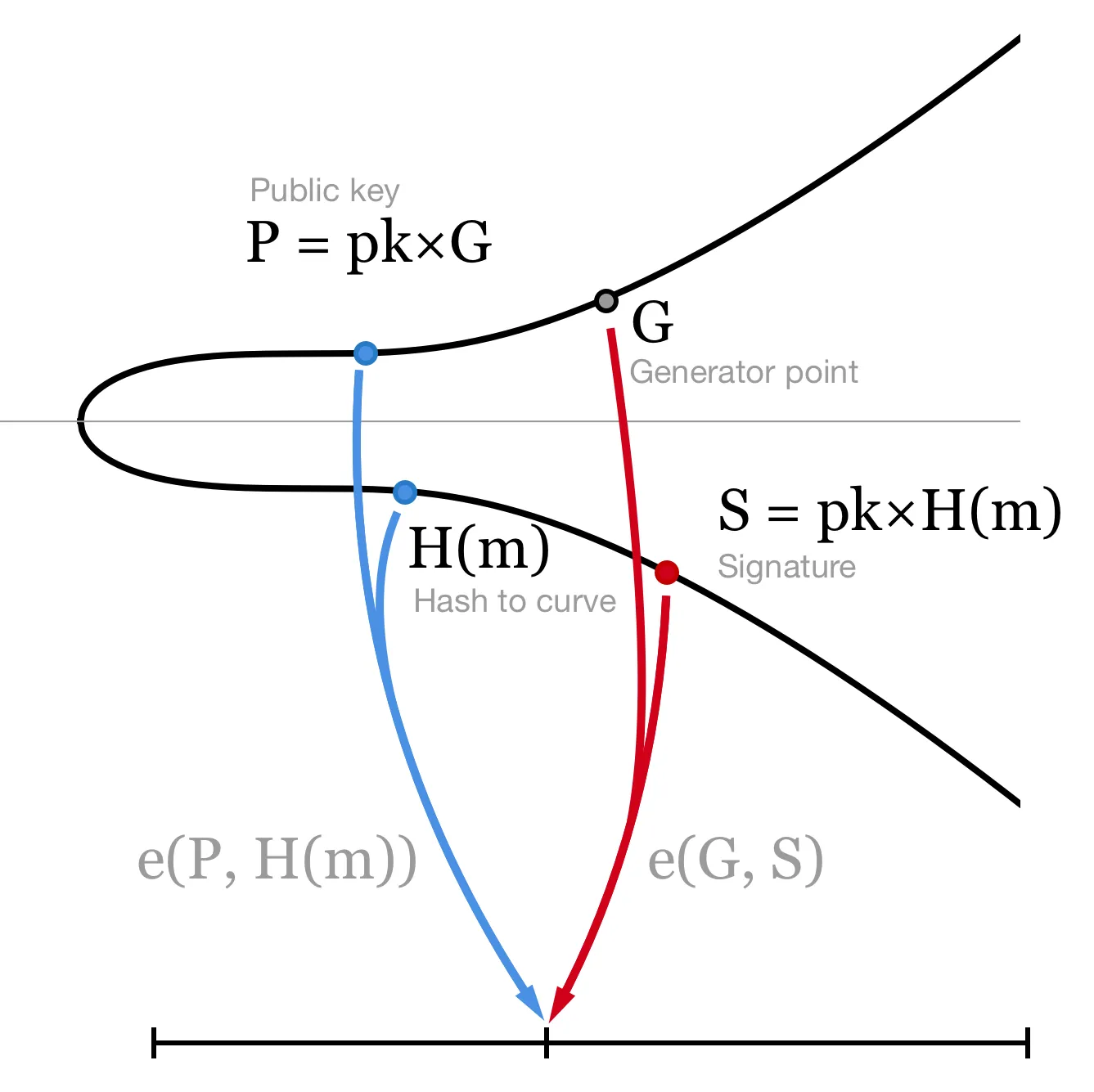
To see why the verification works,
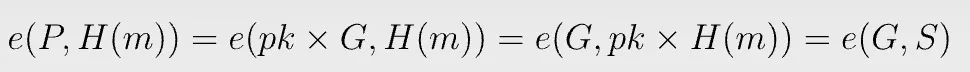
Bilinear pairing e allows us to move scalar pk from the first input to the second.
Implementation on Bitcoin
We have implemented BLS signature verification using the pairing library.
Note we let users pass y-coordinate directly and verify it, to avoid computing modular square root².
Summary
We have only demonstrated how to verify a single BLS signature on Bitcoin. BLS’s main power lies in aggregated signatures and keys. We leave their implementations on Bitcoin as exercises to readers.
***
NOTES:
[1] This approach is called Hash and Pray, which runs in non-constant time. Constant time approach exists, such as Fouque and Tibouchi, but are harder to implement.
[2] We assume a curve point with the x-coordinate exists for ease of exposition here. A hash and pray approach can be easily added.

 07-09-2025
07-09-2025