|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
This post was first published on Medium.
Following our series #1, we demonstrate how to construct and verify Merkle trees using OP_CAT.
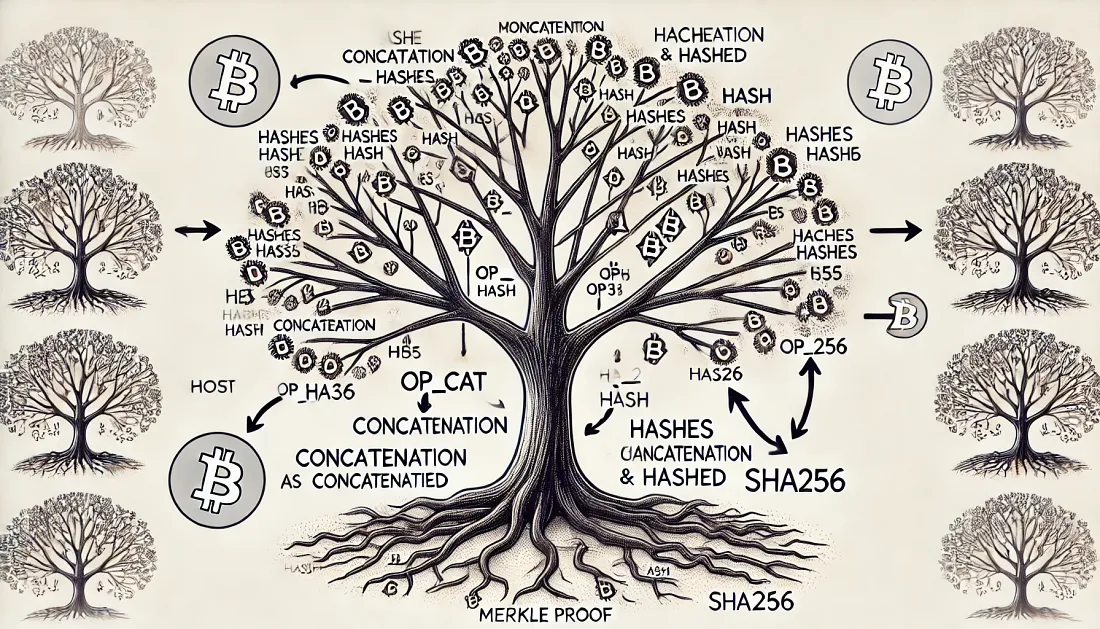
In Bitcoin, Merkle trees are utilized as the data structure for verifying data, synchronization, and effectively linking the blockchain’s transactions and blocks together. The OP_CAT opcode, which allows for the concatenation of two stack variables, can be used with SHA256 hashes of public keys to streamline the Merkle tree verification process within Bitcoin Script. OP_CAT uniquely allows for the creation and opening of entries in Merkle trees, as the fundamental operation for building and verifying Merkle trees involves concatenating two values and then hashing them.
There are numerous applications for Merkle trees. We list a few prominent examples below.
Merkle proof
A Merkle proof is a cryptographic method used to verify that a specific transaction is included in a Merkle tree without needing to download the entire blockchain. This is particularly useful for lightweight clients and enhancing the efficiency of data verification.
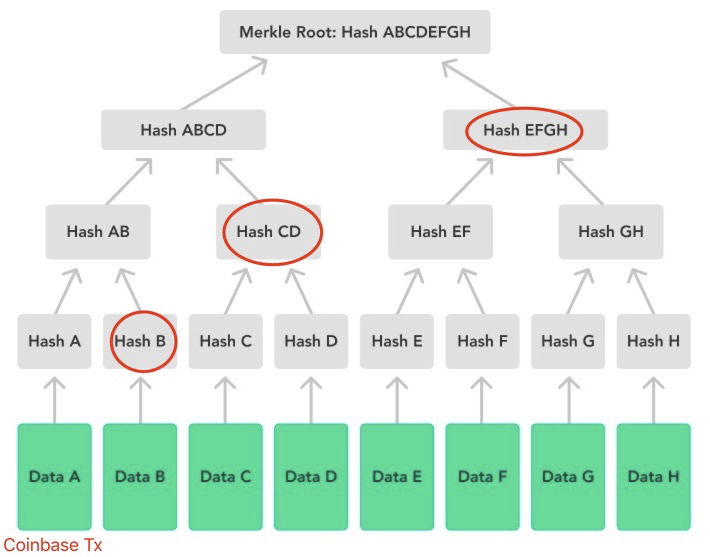
Tree signature
A tree signature is a cryptographic method that enhances the security and efficiency of digital signatures using tree structures, particularly Merkle trees. Compared to regular Multisig, this approach is used to generate a more compact and private proof that a message or a set of messages has been signed by a specific key.
Zero-Knowledge Proof
STARK (Succinct Transparent Arguments of Knowledge) is a type of zero-knowledge proof system. STARKs are designed to allow a prover to demonstrate the validity of a computation to a verifier without revealing any sensitive information about the computation itself. If OP_CAT were to be added to Bitcoin, it could potentially enable the implementation of a STARK verifier in Bitcoin Script, with work already ongoing. This would allow for secure and private transactions on the Bitcoin network. Compared to pairing-based proof systems such as SNARK, STARK is considered to be more Bitcoin-friendly.
Implementation
The implementation of the Merkle tree using sCrypt is trivial. The following code calculates the root hash of a merkle tree, given a leaf and its merkle path, commonly used in verifying a merkle proof.
Full code is at https://github.com/sCrypt-Inc/scrypt-btc-merkle.
A single run results in the following transactions:
- Deploying Transaction ID:
Check the transaction on Mempool
- Spending Transaction ID
Check the transaction on Mempool
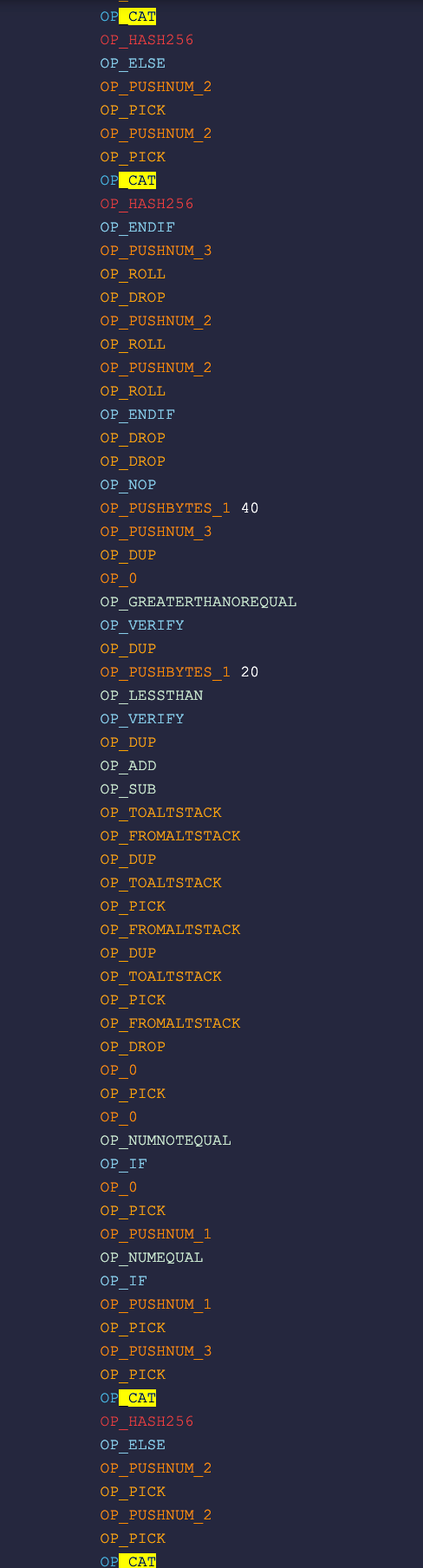
Script versions
There are alternative implementations in bare scripts, like the one below. One significant advantage of using sCrypt for implementing merkle trees is its readability and maintainability. Scripts are often extremely hard to read and work on.
Plz tell me you had a compiler to generate that
— Jerry – Bitcoin Bay (@Lightswarm) March 1, 2024
Stay tuned for more OP_CAT use cases.
Watch: sCrypt Hackathon students realize there’s more to blockchain

 02-26-2026
02-26-2026