|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
This post was first published on Medium.
We have implemented ECDSA signature verification algorithm in Script. It can verify if an arbitrary message is signed by a private key corresponding to a given public key, while OP_CHECKSIG can only verify signatures when the message is the current spending transaction¹. Surprisingly, this is done without introducing any new opcode such as OP_DATASIGVERIFY (aka, OP_CHECKDATASIG) on BCH.
Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA)
ECDSA is the algorithm used in Bitcoin for signature generation and verification. The verification algorithm is listed below.

Implementation
We have implemented the algorithm as shown below, using the elliptic curve library we released before.
First, we need to extract r and s components from the signature, which is encoded in DER format. Since they are big-endian, we have to convert to little-endian, which is how data is encoded in Script/sCrypt.
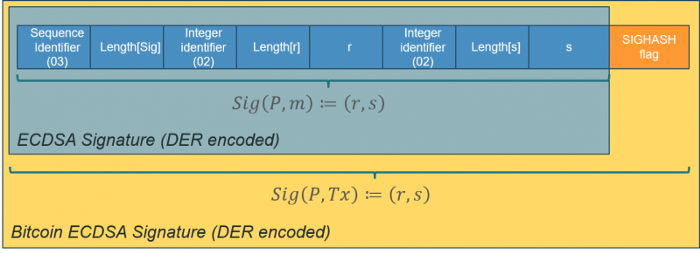
After r and s are retrieved, we simply run the standard ECDSA verification algorithm.
***
NOTE:
[1] More precisely, it verifies signature against sighash.

 03-06-2026
03-06-2026