|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
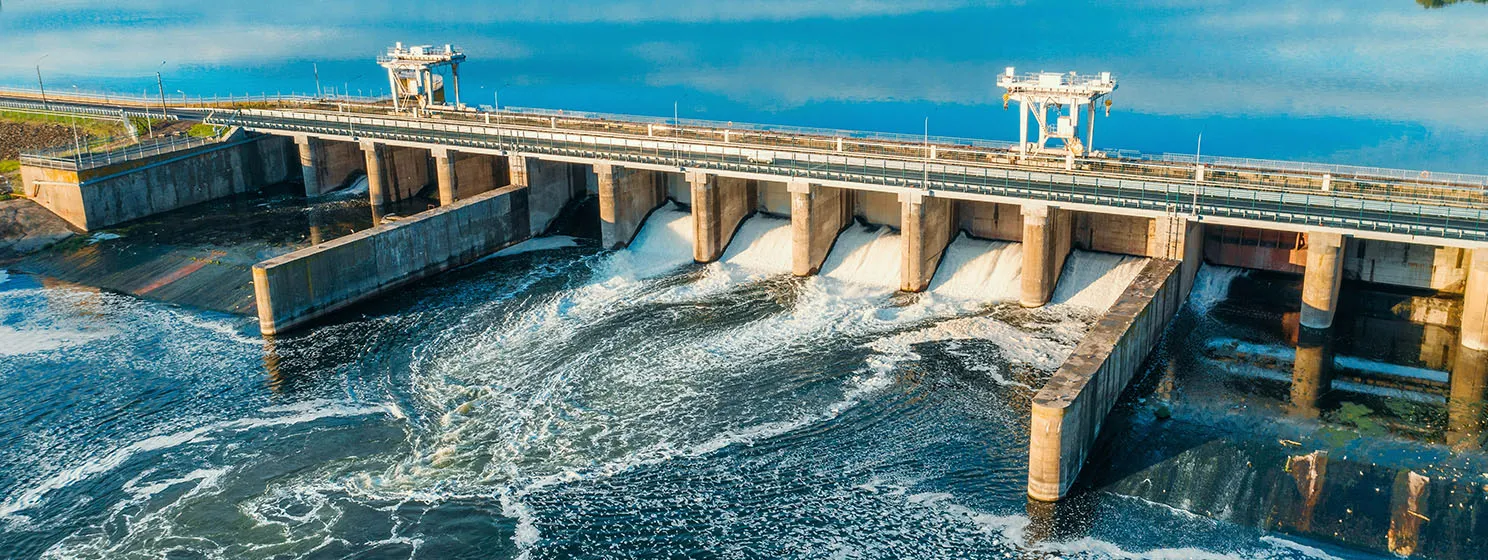
OpenAI, the company behind the market-leading artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot ChatGPT, has filed trademark applications for “GPT-6” and “GPT-7” in China.
The San Francisco company has been embroiled in controversy and infighting, which blew up with the sacking and unexpected re-hiring of CEO and co-founder Sam Altman. However, the trademark applications show that the mission of improving AI continues despite the struggles.
ChatGPT, which boasts 180 million users, launched under the GPT-3.5 multimodal large language model (LLM) a year ago. In March, OpenAI released the improved GPT4.
The company has now filed trademark applications for two extra iterations of its LLM with the China National Intellectual Property Administration, reports the South China Morning Post. This is despite ChatGPT not being available in China or Hong Kong as part of the Chinese government’s “great firewall” that blocks foreign platforms that don’t conform to its censorship laws.
OpenAI filed the trademark applications under class 9, which encompasses scientific and research equipment, and class 42, which covers technology designs and services. The applications were filed under OpenAI OpCo, its parent entity.
The trademark applications are forward-looking at best. In addition to being barred from officially serving Chinese users, OpenAI has yet to receive approvals for GPT-4, Whispers, and GPT-5 trademark applications. It applied for the first two in April and the other in July.
OpenAI has revealed scant details about future iterations of its LLM. However, in a November interview, Altman revealed that the new version would be more capable than its predecessors, although he declined to give a release date. The company is banking on more funding from Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT)—which has already invested $10 billion in the $29 billion-valued startup—to cover training costs for GPT-5.
The initial version of the LLM, GPT-3, was built from 175 billion parameters, which are the components that influence its functioning. While OpenAI didn’t disclose how many parameters GPT-4 has, reports claimed it was over a trillion. GPT-5 is expected to have much more parameters and be more capable.
As ChatGPT chases trademarks in China, its local rivals are investing billions to give China’s 1.4 billion residents an alternative. Baidu, China’s Google (NASDAQ: GOOGL) replica, is leading the race with its Ernie chatbot that launched in late August.
However, in China, chatbots must adhere to the government’s stances on key issues, including COVID-19, the Russian-Ukraine conflict, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and more. One AI chatbot version developed by a Microsoft spin-off changes the subject or claims to be tired when asked about such sensitive topics.
In order for artificial intelligence (AI) to work right within the law and thrive in the face of growing challenges, it needs to integrate an enterprise blockchain system that ensures data input quality and ownership—allowing it to keep data safe while also guaranteeing the immutability of data. Check out CoinGeek’s coverage on this emerging tech to learn more why Enterprise blockchain will be the backbone of AI.
Watch: Artificial intelligence needs blockchain

 07-12-2025
07-12-2025